Dates as data
Authors:Christie Bahlai, Aleksandra Pawlik
Contributors: Jennifer Bryan, Alexander Duryee, Jeffrey Hollister, Daisie Huang, Owen Jones, and Ben Marwick
Learning Objectives
- Understanding how dates are handled and formatted in spreadsheets
- Manipulating dates stored in spreadhseets
- Understanding the caveats of the default formatting of the dates
Dates in spreadsheets are stored in one column. Whilst this seems the most natural way to record dates, it actually is not a good practice. A spreadsheet application will display the dates in seemingly correct way (for the human eye) but how it actually handles and stores the dates may be problematic.
Let’s try with a simple challenge.
Challenge: pulling month, day and year out of dates
- In the
datestab of your Excel file you have the data from 2014 plot 3. There’s aDate collectedcolumn. - Let’s extract month and year from the dates to new columns. For this we can use the built in Excel functions
=MONTH(A3)
=DAY(A3)
=YEAR(A3)
(Make sure the new column is formatted as a number and not as a date.)
You can see that even though you wanted the year to be 2014, Excel automatically interpreted it as 2015, the year you entered the data.
Preferred date format
Instead it is much safer to store dates with MONTH, DAY and YEAR in separate columns or as YEAR and DAY-OF-YEAR in separate columns.
Note: Excel is unable to parse dates from before 1899-12-31, and will thus leave these untouched. If you’re mixing historic data from before and after this date, Excel will translate only the post-1900 dates into its internal format, thus resulting in mixed data. If you’re working with historic data, be extremely careful with your dates! Excel also entertains a second date system, the 1904 date system, as the default in Excel for Macintosh. This system will assign a different serial number than the 1900 date system. Because of this, dates must be checked for accuracy when exporting data from Excel (look for dates that are ~4 years off).
Data formats in spreadsheets
Spreadsheet programs have numerous “useful features” which allow them to “handle” dates in a variety of ways.
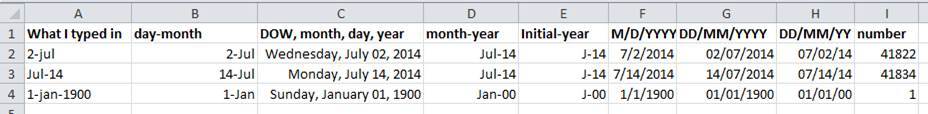
But these ‘features’ often allow ambiguity to creep into your data. Ideally, data should be as unambiguous as possible.
Dates stored as integers
The first thing you need to know is that Excel stores dates as a number - see the last column in the above figure. Essentially, it counts the days from a default of December 31, 1899, and thus stores July 2, 2014 as the serial number 41822.
(But wait. That’s the default on my version of Excel. We’ll get into how this can introduce problems down the line later in this lesson. )
This serial number thing can actually be useful in some circumstances. Say you had a sampling plan where you needed to sample every thirty seven days. In another cell, you could type:
=B2+37
And it would return
8-Aug
because it understands the date as a number 41822, and 41822 +37 = 41859 which Excel interprets as August 8, 2014. It retains the format (for the most part) of the cell that is being operated upon, (unless you did some sort of formatting to the cell before, and then all bets are off).
Which brings us to the many different ways Excel provides in how it displays dates. If you refer to the figure above, you’ll see that there are many, MANY ways that ambiguity creeps into your data depending on the format you chose when you enter your data, and if you’re not fully cognizant of which format you’re using, you can end up actually entering your data in a way that Excel will badly misinterpret.
Question
What will happen if you save the file in Excel (in csv format) and then open the file using a plain text editor?
Note
You will notice that when exporting into a text-based format (such as CSV), Excel will export its internal date integer instead of a useful value (that is, the dates will be represented as integer numbers). This can potentially lead to problems, if you use other software to manipulate the file.
Advantages of Alternative Date Formatting
Storing dates as YEAR, MONTH, DAY
Storing dates in YEAR, MONTH, DAY format helps remove this ambiguity. Let’s look at this issue a bit closer.
For instance this is a spreadsheet representing insect counts that were taken every few days over the summer, and things went something like this:
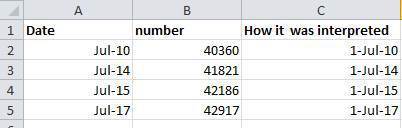
If Excel was to be believed, this person had been collecting bugs IN THE FUTURE. Now, we have no doubt this person is highly capable, but I believe time travel was beyond even his grasp.
Entering dates in one cell is helpful but due to the fact that the spreadsheet programmes may interpret and save the data in different ways (doing that somewhat behind the scenes), there is a better practice.
In dealing with dates in spreadsheets, we recommend separating date data into separate fields (day, month, year), which will eliminate any chance of ambiguity.
Storing dates as YEAR, DAY-OF-YEAR
There is also another option: You can also store dates as year, and day of year (DOY). Why? Because depending on your question, this might be what’s useful to you, and there is practically no possibility for ambiguity creeping in.
Statistical models often incorporate year as a factor, to account for year-to-year variation, and DOY can be used to measure the passage of time within a year.
So, can you convert all your dates into DOY format? Well, in Excel, here’s a handy dandy guide:
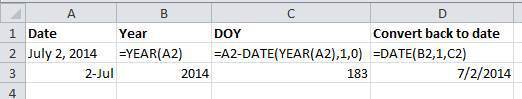
Previous: Formatting problems Next: Basic quality control and data manipulation in spreadsheets.
